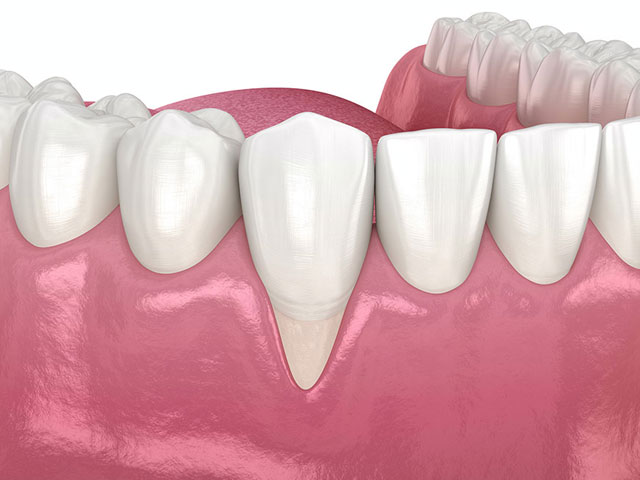
What is gum recession?
The tooth gum (also called gingiva) is the skin that covers the inside of the upper and lower jaw and the teeth. Recession of this skin is when the gum tissue covering the teeth pulls back, exposing the tooth or tooth root. As a result of gum recession, spaces are formed between the teeth and the gum line (gum pockets). Bacteria can easily accumulate in these pockets and speed up gum recession.
If this issue is left untreated, the tissue and bone structures that support the teeth can be severely damaged and tooth loss can occur. Research shows that gum recession affects one in every two people worldwide.
What are the symptoms of gum recession?
This disease is a common dental problem and can affect people of all ages. The first symptom of it is usually tooth sensitivity. Apart from this, the symptoms of receding gums can be listed as follows:
- Bleeding gums
- Bleeding observed when eating hard foods (such as apples, pears)
- Longer looking tooth
- Redness or swelling of the gums
Why do gums recede?
Receding gums can be the result of many different conditions:
Poor or improper dental care: Poor dental care causes tartar plaque to build up between the teeth. Tartar is a very hard substance that sticks to your teeth and gums and can only be removed by professional dental cleaning. Improper dental care however is simply doing it wrong. Brushing the teeth very hard is the most common type of improper dental care.
Genetic factors: Studies have shown that one third of the population suffers from receding gums even with regular dental care.
Periodontal diseases: Bacterial formations that can destroy the gum tissue and the jaw bone are called periodontal diseases. They are the top cause of gum recession and many other tooth and mouth related problems.
Hormonal changes: Biological processes such as puberty, pregnancy, breastfeeding and menopause cause hormone levels to fluctuate, making the gums more sensitive than usual. Gum recession and tooth related complaints are very common during these periods.
Using tobacco products: Tobacco users are more likely to have sticky plaque on their teeth that is difficult to remove and can cause gum recession.
How is gum recession treated?
Treatment for mild cases is done by deep cleaning the affected area. During a deep cleaning, plaque and tartar that has formed below the gum line is carefully removed and the exposed root area is smoothed to make it harder for bacteria to take hold. When gum recession is extreme, gum surgeries may be required. The most effective of these is graft surgery. In this procedure, tissue is taken from the upper palate or another donor site and sutured to the gum tissue surrounding the exposed root lines.
How to prevent gum recession?
- Brushing your teeth at least 2 times every day is the basic way to get rid of tooth problems
- Cleaning gum pockets with dental floss or similar products clean the parts which brushes can’t reach
- Visiting your dentist at least twice a year -even if you have no complaints- can make you learn approaching problems
- Observing your gums periodically can give you clues about the health of your gum tissue
- Following proper treatment for your chronic problems (e.g. diabetes) also eases your mouth care

